How to introduce a brand to the Asian market, using China as an example? China is an intriguing alternative for corporate expansion, given its position as the biggest trade nation in the world and its GDP of more than $10 trillion. When developing a brand in China, however, businesses cannot merely rely on the marketing methods they have used in Western cultures because these strategies are inappropriate for the Chinese market. It’s possible that the local Chinese market won’t respond well to these marketing efforts.
Everything is different in China, from how customers locate a company to the social media channels utilized to the guidelines governing conducting business there. It is essential to have a solid understanding of these distinctions.
This Post will review some of the most effective strategies for entering the Chinese market. In addition, we will discuss some of the difficulties you can experience and offer advice on how to get beyond them. Continue reading this article if you consider growing your company’s operations in China.
- Why is it crucial to enter the Chinese market in 2023?
- Rules of Marketing in China
- 10 Strategies to Introduce your brand in China.
- Case Studies and Success Stories
- Conclusion
Why is it crucial to enter the Chinese market in 2023?
The use of digital marketing is more widespread than it has ever been in China, and businesses there are developing innovative approaches to capitalize on this trend. Everything has been impacted due to the Covid-19 outbreak, including how people search for information, communicate with one another, and even shop. As a consequence of this, companies need to rethink the way they promote their products to consumers and come up with innovative ways to cultivate client loyalty.
Investing in China is not always easy, but no other country can take China’s place as a market leader. China’s market continues to provide immense growth potential. China is the most populated country in the world thanks to its population of over 1.412 billion people. This indicates that about one in every five people on Earth lives within this thriving economy. It is anticipated that within the next ten years, Chinese consumer expenditure will nearly double, emphasizing services rather than items.
How to Enter the Chinese Market?
Entering the Chinese market takes forethought and the ability to adjust to the country’s specifics. Conducting extensive market research to understand consumer behavior and trends, developing a tailored market entry strategy, establishing local partnerships, localizing your brand and marketing materials, protecting intellectual property, leveraging digital marketing platforms, adapting to regulatory requirements, and building trust and reputation are some key steps. These measures form the basis for penetrating the dynamic Chinese market and expanding your business there.
What are some of the difficulties of carrying out this activity, and how can these be overcome?
China is still one of the world’s greatest markets and has tremendous untapped potential. However, if you lack the necessary knowledge, conducting business in this industry can be difficult. Companies that are based in countries other than China often struggle with problems related to regulatory compliance.
These problems can include a lack of time to comply with newly introduced legislation or a fragmented approach to meeting local regulatory requirements. Companies that want to export to China must also contend with favoritism against local competitors, cultural obstacles, the demand to localize products or services, and communication methods to match the standards and demands of Chinese consumers.
Understanding the Chinese Market
1. Market potential and size
With a population of more than 1.4 billion population, China offers brands an unrivaled market size and opportunity. The sheer volume of customers is a huge opportunity for firms looking to grow. The size of the Chinese market can strongly impact the development and success of a brand.
In addition, consumers’ spending power has expanded due to China’s growing middle class. The demand for high-quality goods and services increases as disposable incomes rise, fostering a favorable atmosphere for firms to prosper.
Additionally, China has experienced a boom in recent years in e-commerce, with a considerable shift toward online purchasing. Online stores like Alibaba’s Tmall and JD.com have become the main venues for customer transactions. Through this digital shift, brands have more ways to connect with and engage Chinese consumers.
2. Consumer preferences and behavior
A trend toward a consumer-driven economy best describes China’s changing consumer landscape. Brands must comprehend and adapt to Chinese consumers’ preferences to flourish in the market, as they have a more educated and sophisticated client base.
Chinese consumers heavily rely on social proof and recommendations when making decisions. Word-of-mouth, online reviews, and recommendations from friends and family greatly influence purchase decisions. Trust and loyalty are created by establishing a brand reputation and promoting pleasant consumer experiences.
Chinese consumers are renowned for prioritizing their mobile devices. Due to the high smartphone penetration rate, mobile devices are essential to their daily lives. To provide customers with seamless and interesting experiences, brands must adapt their marketing tactics for mobile platforms.
The Chinese market places a high priority on convenience. Chinese shoppers prioritize ease in purchasing choices, favoring streamlined shopping experiences and quick delivery options. Brands that provide simple, effective, and customer-focused experiences benefit from a competitive advantage.
3. Cultural factors influencing brand perception
For a company to successfully enter the Chinese market, it is essential to comprehend the cultural influences on brand perception. Chinese society’s rich cultural legacy and customs affect consumer behavior and brand preferences.
In China, collectivism is a significant cultural virtue. Chinese customers frequently place their social networks’ experiences and views above personal preferences. To increase their attractiveness, brands should take advantage of social connections and promote a sense of community.
In China, upholding the culture of face-saving and social harmony is crucial. Negative events or public disputes can greatly impact how consumers perceive brands and their trustworthiness; therefore, businesses must be careful about reputation management.
In Chinese culture, superstitions and lucky/unlucky numbers are significant. Brands should be conscious of cultural icons and avoid any connotations that could be interpreted unfavorably or unlucky.
4. Current state of the economy and technology
Regional market variances are a product of China’s quick urbanization. Each location has distinct consumer and economic characteristics, calling for customized market entry and growth methods.
China has one of the greatest internet adoption rates globally, with a sizable population accessing the internet. Social media, online platforms, and e-commerce have assimilated into consumers’ daily life. To reach and interact with their target audience, brands should use these digital channels to their full advantage.
The Chinese market has transformed because of technological improvements, particularly mobile payments. Cashless transactions are now the norm because of the increasing adoption of platforms like WeChat Pay and Alipay. To accommodate these widely used mobile payment options, brands must modify their payment systems.
The Chinese government aggressively promotes the technology and innovation industries, encouraging entrepreneurship and R&D. This fosters technical development and allows brands to work with regional partners or take advantage of government initiatives.
For a brand to be successfully introduced in China, it is essential to comprehend the Chinese market’s distinct features, consumer habits, cultural influences, and economic and technological environment. Businesses can position themselves for growth and success in the dynamic Chinese market by adjusting strategies to match these variables.
Rules of Marketing in China
Even if you might have a fantastic product, it alone will not guarantee that you will successfully sell it in the Chinese market. Because there are so many different products and companies in China, it is essential that you can differentiate yourself from others and understand some basic rules. It is necessary for you to have a marketing plan and strategy that is tailored to China.
1. Regulations Regarding Digital Advertising in China
Stringent regulations govern access to the Internet in China. Customers are unable to access a significant number of the websites that are common in other parts of the world. Popular websites in China, such as Google, Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube, are unavailable to the general public.
You will need to promote on channels that are easily accessible and well-liked in China if you want your digital marketing strategy to be successful. The primary channels that you should focus on advertising on are as follows:
- WeChat.
- Sina Weibo.
- Baidu.
- Tencent Channels.
- Toutiao.
However, the procedure does not just involve using these channels in the way you may be accustomed to doing so in Western societies.
2. E-Commerce Rules in China
Numerous businesses have expressed an interest in penetrating the massive Chinese market, which comprises more than 1.3 billion end users. With a share of 30 percent in the international e-commerce sector, China is home to the greatest population of online buyers anywhere in the world. The value of goods sold online in China currently surpasses 8.8 trillion RMB.
More than $25 billion worth of goods were purchased through e-commerce on a single day when consumers were encouraged to shop. In light of these enticing statistics, many companies hope to join the ranks of those who have already successfully introduced their product in China. Any company that wishes to advertise in China is required to obtain a license from the Chinese government.
To lawfully advertise a product or service in China, a company must obtain a local advertising license, even if it is not required to have a sales license to sell products in China. Working with a trade partner who can market their product through their TMall or JD shop is one strategy that some companies employ to sidestep this requirement.
3. Government Policies and Regulations
Government rules and policies significantly impact how China’s economic climate is shaped. One must comprehend and adhere to these policies for successful market entry and operation. Here are some significant factors to think about regarding Chinese government policies and rules:
Regulations for Foreign Investment: China has distinct rules governing foreign investment. The government has implemented several measures to promote foreign investment in particular industries while controlling delicate industries. It is critical to comprehend the laws and guidelines governing foreign ownership, the methods for approving investments, and the limitations of particular industries.
Intellectual Property Protection: Intellectual property (IP) protection is a major problem for companies entering the Chinese market. China has worked to improve IP laws and enforcement practices. Nevertheless, taking the necessary precautions to safeguard your brand, trademarks, patents, and copyrights is still essential. This can entail requesting IP protection in China and taking steps to stop infringement.
Regulations for Import and Export: China has certain rules for all import and export operations. Customs processes, tariff requirements, product standards, and labeling laws must all be followed. To maintain seamless operations and prevent any legal concerns, it is essential to understand the documentation and licensing requirements for importing and exporting commodities.
Employment and Labor Laws: Contracts, working hours, pay, social insurance contributions, and employee benefits are governed by labor laws and regulations in China. Compliance with labor rules is crucial to avoid legal issues and have a good working relationship with employees.
Levies and Financial Regulations: China has a complicated tax system comprising many levies, including value-added tax (VAT), corporate income tax, and others. Comprehending the tax liabilities, reporting requirements, and business-friendly tax benefits is critical. Financial rules and reporting standards must also be observed, including utilizing reputable accounting methods and making full financial disclosures.
Regulations by Industry: Various industries may have rules and license requirements. To ensure compliance with industry-specific standards and safeguard consumer interests, additional rules are in place in the pharmaceutical, healthcare, telecommunications, and financial sectors. It is crucial to be aware of and follow these rules unique to your sector.
Environmental legislation: China has been actively tightening its environmental legislation to combat pollution and advance sustainable development. Businesses must abide by laws, rules, and standards about environmental protection, which may involve getting licenses, managing trash, and putting in place pollution control measures.
Navigating China’s complicated laws and regulations requires careful attention and knowledge. To ensure compliance and reduce any potential risks, it is advisable to collaborate with legal and regulatory consultants with expertise in Chinese law. Businesses can flourish in the Chinese market by adapting to regulatory changes and adopting a proactive attitude.
China’s Platforms and Channels for Digital Marketing
These channels each have their own set of guidelines and expectations. For instance, to begin purchasing advertisements on Baidu and creating an account, you must first pay a minimum deposit of 30,000 RMB.
You need to obtain a current license from the relevant industry before participating lawfully in any form of digital advertising. In addition, most fields have stringent regulations that govern the kinds of advertisements that can be published.
For instance, if you plan to sell health and supplement items within the country’s borders, you must get a license designed specifically for this purpose. Because certain platforms do not permit accounts to be created by users from outside of the country, you could be required to go through a partnered agency that will handle the management of your account and serve as your media buyer.
Many companies collaborate with an agency rather than take responsibility for their advertising account. To gain improved help from some channels, you must spend a particular amount of money each month on the associated account.
Best Provinces of China to Introduce Your Brand
| Province | Key Industries |
| Shenzhen | Information technology (IT), communications, biomedicine, semiconductors, electronics information |
| Shandong | Pharmaceuticals, Agricultural products, oil & foodstuffs |
| Shanghai | Petrochemicals, chemicals, automobiles, pharmaceuticals, electronic apparatus, financial services |
| Jiangsu | Textiles, chemicals, petrochemicals, food, biomedicine, auto parts, Steel |
| Beijing | Information technology (IT), communications, electronics |
| Zhejiang | Plastics, textiles, kitchenware, apparel, metallurgy, toys, Light industry, household electrical, furniture |
| Guangzhou | Chemicals, electronic appliances, petrochemicals, toys, textiles, automobiles, apparel |
10 Strategies to Introduce your brand in China.
To successfully reach and engage with the target audience in China, the introduction of your brand requires a strategy that has been meticulously designed. When thinking about breaking into the Chinese market, here are 10 different techniques to consider:
1. Use Baidu or PPC/SEM Campaigns to Get Visibility.
Baidu has already eclipsed Google as the biggest search engine and currently holds an approximately 86% market share. Whenever a Chinese person needs to look something up, they go to Baidu. It is essential to your success in marketing in China that you have a solid understanding of Baidu, equivalent to Google in China.
How to register a company in China in 2023 Watch this video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xe0SmwMXRzM
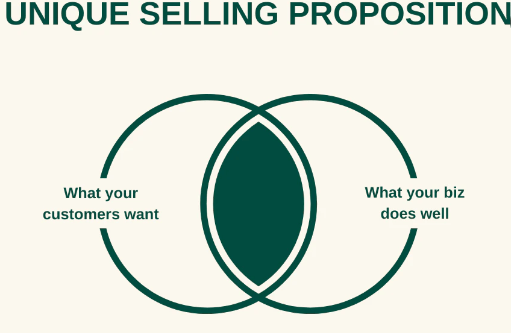
2. Develop a Localized Unique Selling Proposition
Bands must remember that the items and services trending on Instagram (or other global media channels) might not be all that popular in China, and vice versa. This is something that they should be aware of. The Chinese market is vital for most luxury businesses and brands that produce digital products, like Apple.
These firms cater to consumers on the go, like Starbucks, lifestyle brands like Ikea, and many more. However, it is also important to highlight that all of these brand triumphs came from the company’s experience and grasp of the various requirements of different international markets.
What steps can you take to ensure that your company’s goods or services are adapted to the needs of the Chinese market?
- Gain an understanding of the purchasing patterns and how business is conducted in China, particularly in your sector.
- Do not limit yourself to desk research; instead, organize a focus group to understand the Chinese consumer’s perspective better. Please include as many questions as possible about your product or service, ranging from the packaging to the usage, to the customer journey and experience, to why individuals would recommend or not suggest your product or service to their friends.
- Make use of the information gathered, and make any necessary adjustments to the product or service before releasing it onto the market.
3. Hiring Staff
It is debatable that the caliber of a company’s workforce is the biggest factor in determining its ultimate success in China. The sort of business will frequently decide the human resources that are accessible, and international businesses typically have greater autonomy with WFOEs and representative offices than JVs in this regard.
The location of the business will strongly influence the availability of high-quality human resources; in general, Tier One cities, such as Shanghai and Beijing, have substantially better human resource availability than Tier Two and Tier Three cities.
Another important choice is hiring foreigners for senior management jobs or localizing these positions. Employing expatriates is frequently viewed as providing more operational control, but it is also more expensive regarding compensation packages, moving expenses, insurance, and other costs.
Additionally, most foreign managers have a very limited understanding of local Chinese business and cultural customs and seldom possess the Chinese language proficiency required to interact with Chinese businesses regularly.
Employing a Chinese manager has many advantages, including their grasp of the local market and Chinese company in depth. Chinese workers have frequently established contacts (‘guanxi’) with suppliers, consumers, and local government agencies that can be fully leveraged and have reduced wage and insurance costs.
4. Gain Chinese consumers’ trust by staying on trend
The ability to purchase luxury goods is mostly determined by one’s purchasing power, which is also a key role in forming a consumer mentality. The survey’s findings suggest that Chinese consumers are willing to splurge, as they have more disposable income and a growing desire for high-end goods due to the country’s rapid economic progress.
They are anxious to buy luxury items as a method of social development and the expression of personality, and they are heavily impacted by the content of the media in their decision-making processes regarding purchases.
The generation known as Gen Z is swiftly becoming the most important consumer base for luxury companies, and their tendency to shop is fairly strong. According to the poll findings, 21% of respondents in the Gen Z age bracket are willing to spend more than 16% of their earnings on luxury items.
This is a relatively high percentage for individuals who have just recently finished their first degree or entered the workforce for the first time. They prefer to make their purchases through important e-commerce platforms and the official channels offered by the company.
Pablo Mauron, Partner and Managing Director of China, DLG (Digital Luxury Group), says:
“Until the Personal Information Protection Law (PIPL) went into effect in 2021, major brands could get by in China with an expanded version of their worldwide CRM infrastructure. As a result of these new restrictions, organizations must rethink their consumer data infrastructure to comply with local laws and maximize performance. This is especially crucial at this point when customer retention and life cycles are more in the spotlight for brands.”
5. Working Together with Influencers
Due to netizens’ propensity to share and remark on what they see online, content can spread swiftly in China. Influencers are the place to go if you want many people to view your content because they appreciate expert opinions and seek them out.
Both small and large enterprises can employ Chinese influencer marketing. Smaller brands can use it to attract the attention of their target market and raise awareness. Working with influencers is especially advantageous for e-commerce companies because platforms like WeChat stores frequently have low traffic. Influencer marketing can boost your products’ visibility and revenues by sending buyers to your page.
Given that influencers offer material that users have found beneficial, consumers are more receptive to this sort of marketing since influencers are more approachable and relevant.
6. Learn about the Customer Journey in China
The conversion funnel and consumer buying patterns for various goods and services in China must be considered when entering the Chinese market. A company’s target market’s cultural norms and lifestyle should be considered while developing a marketing strategy.
Is your product better suited for RED (Xiaohingshu) or WeChat Mini-program users? It would be best if you learned who uses these apps and why to respond to this question. It is critical to understand the demographics of the platforms and apps most popular in China, including the business focus, ideal industries, and other factors. Brands must comprehend every facet of their target market’s lifestyle and work to integrate themselves into it.
7. The Development of An International Property Rights (IPR) Strategy
Protecting your brand and inventions in this significant market requires developing an effective intellectual property rights (IPR) strategy for China. The first step is understanding Chinese IP regulations governing trade secrets, patents, copyrights, and trademarks. To operate the system efficiently, familiarize yourself with the registration processes and enforcement practices.
Make filing for IP protection in China a top priority and concentrate on trademarks and patents pertinent to your company. Working with a Chinese IP lawyer can ensure accurate and prompt filings with the various government offices.
Consider defensive trademark registrations outside of your primary business to protect your IP. This helps avoid trademark squatting, a problem in China, and unlawful use.
Put monitoring procedures in place to find potential violations. Watch for illicit use of your IP on websites, at trade events, and in actual stores. When there is a violation, move quickly to enforce your rights, using legal means if required. Work with Chinese customs officials to prevent the sale of fake goods. Register your intellectual property rights with customs to make it easier to seize counterfeit goods at crossings.
Build contacts with regional IP enforcement agencies to secure their cooperation and assistance in IP enforcement efforts. Inform them of your intellectual property rights while proactively engaging with them.
8. Online and Offline Commerce in China
An emerging strategy in Chinese e-commerce is the online-to-offline (O2O) model, which leverages the best of both worlds by merging the reach of the Internet with brick-and-mortar storefronts.
2016 began the true O2O online-to-offline commerce revolution that industry leader Alibaba launched. Alibaba founder Jack Ma made the “New Retail” announcement at a conference in Hangzhou, showing his commitment to expanding the company’s business model beyond online sales. This idea created a cohesive data chain from previously separate online, offline, and logistical components.
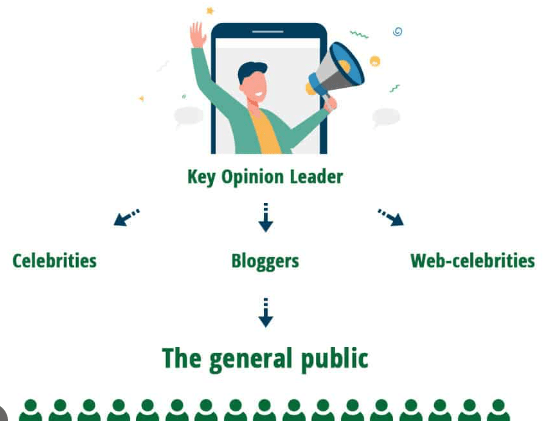
9. Utilize Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs)
You may make a powerful first impression on the Chinese market by introducing your brand in a way that uses Key Opinion Leaders (KOLs), which you can utilize in your marketing plan. KOLs have built a big social media following and established themselves as credible experts or influencers in a certain industry.
Promoting a brand can be improved through collaboration with Chinese KOLs. To begin, KOLs have a devoted and engaged audience that trusts their recommendations and opinions. When a key opinion leader (KOL) endorses or recommends your brand, it can instill a powerful sense of legitimacy and trust in your company among its followers.
In addition, KOLs typically have a profound comprehension of the people who make up their audience, and they can provide invaluable insights into consumers’ preferences, behaviors, and trends. You will be able to obtain vital market insights through working with them, and you will also be able to modify your brand messaging and marketing activities so that they resonate with the target demographic.
In China, key opinion leaders, or KOLs, come in various forms. These include celebrities, industry experts, lifestyle influencers, and social media personalities. You may be able to find and collaborate with key opinion leaders (KOLs) who share your brand’s values and have a significant amount of sway over your target audience, but this will depend on your brand and your target market.
Creating a relationship with KOLs that benefits both parties when cooperating with them is crucial. You should offer them content exclusive to their audience, engaging, exclusive access to your products or services, and incentives to share their experiences with their audience. This may take the form of sponsored blogs, reviews of products, live streaming sessions, or even cooperation on special events or marketing initiatives.
Rather than selecting KOLs based on the number of followers they have, it is essential to look for individuals who have a true connection to your company and the people you intend to market to. To ensure that KOL’s endorsement comes across as real and believable to its audience, the partnership must be relevant and authentic.
In addition, you should keep track of how well your collaborations with KOLs are performing and the impact they are having. It is important to keep track of metrics like engagement, reach, conversions, and sentiment analysis to evaluate how successful the partnership’s success is regarding future partnerships informed by data.
When taken as a whole, capitalizing on the impact and reach of key opinion leaders (KOLs) in the Chinese market can greatly enhance a brand’s awareness, legitimacy, and engagement levels. You may successfully expose your brand to the target audience and establish a positive perception that promotes business growth if you collaborate with the appropriate KOLs and develop meaningful partnerships.
10. Stay abreast of regulatory changes
Staying current on regulatory developments is essential when launching a brand in the Chinese market. Businesses must keep aware and adapt due to the regulatory environment in China, which is recognized for its constant updates and changing policies. Keeping up with regulatory changes is essential, and here are some tips for doing so:
- Ensuring Compliance: Regulatory compliance is crucial for companies doing business in China. Regulation non-compliance may result in penalties, legal ramifications, or even the suspension of operations. You may ensure that your company operates within the law’s parameters, safeguarding your reputation and reducing risks by keeping up with regulatory developments.
- Navigating Industry-Specific rules: In China, certain industries may be subject to rules that are unique to those industries. For instance, specific regulations and licensing standards apply to these industries’ healthcare, financial, and e-commerce sectors. To maintain compliance and prevent any business interruptions, staying on top of certain requirements particular to your industry is essential.
- Risk and Challenge Mitigation: By being aware of regulatory changes, you can proactively recognize and address any risks and difficulties. By remaining educated, you can predict how new legislation may affect your business operations, supply chain, marketing plans, or intellectual property rights. This allows you to create backup plans, modify your business procedures, and lessen any detrimental effects on your brand.
- Participating in Industry Associations and Networks: Industry associations and networks can offer insightful information on regulatory developments. Participate in conferences and seminars, join the relevant industry associations in China and network with specialists in the field. These venues frequently include updates on legislative changes, compliance advice, and discussions on best practices.
- Building Relationships with Regulatory officials: It might be helpful to navigate regulatory changes to develop relationships with Chinese regulatory officials. Actively interact with the appropriate government agencies, attend workshops or informational sessions, and, if necessary, ask for clarification on new regulations. These connections may be able to impact policy choices and aid in your knowledge of regulatory expectations.
- Engaging Legal and Regulatory Experts: Working with regional legal and regulatory specialists can be quite helpful when managing regulatory changes. They may assist with interpreting new rules, determining how they will affect your company, and providing advice on compliance tactics. Working with experts familiar with Chinese legislation can save time, effort, and legal issues.
- Internal Process Implementation and Training: Setting up internal procedures and processes to keep track of regulatory changes is crucial. Give charge of keeping track of updates, evaluating their effects, and communicating essential organizational changes to specified people or teams. Additionally, hold frequent training sessions to inform staff members of new laws, compliance standards, and best practices.
You may successfully negotiate the difficulties of the Chinese market by keeping a close eye on regulatory developments and making adjustments as necessary. Your brand may maintain a strong position in the market while reducing potential risks and problems brought on by regulatory changes by being informed, participating in industry networks, consulting with experts, and establishing internal compliance practices.
Case Studies and Success Stories
Many brands have had impressive success breaking into the Chinese market. Here are a few more instances:
Nike: Nike has been able to capitalize on China’s expanding fitness and sports cultures. They interacted with prominent local athletes and supported high-profile events, strongly connecting them to athleticism. Nike’s marketing initiatives incorporated Chinese culture and values, which resonated with customers and helped the company establish itself as a representative of urban youth culture.
BMW: By comprehending the aspirational desires of Chinese consumers, BMW developed a significant presence in China. They targeted the newly developing rich class by positioning their cars as a status symbol. Additionally, BMW customized its marketing strategies, displaying Chinese scenery and adding Chinese design cues into its opulent showrooms.
KFC: KFC pioneered the Chinese market and adapted its menu to suit regional preferences. They included menu items like congee, and Chinese-style fried chicken to cater to the Chinese palate. KFC has become a well-liked fast-food brand in China due to its intensive localization efforts, which include Chinese holiday celebrations and adjusting to local preferences.
Alibaba: The Chinese e-commerce behemoth has completely changed how people shop online in China. By comprehending Chinese consumers ‘ demands and difficulties, Alibaba developed Taobao and Tmall, platforms offering a seamless online shopping experience. Their creative business models, such as the Singles’ Day shopping extravaganza, have seen great success and elevated Alibaba to the top of China’s e-commerce hierarchy.
Conclusion
B2B organizations may find it frightening to enter the Chinese market due to the numerous difficulties and dangers it provides. The benefits of navigating the market, however, are tremendous. The advantages of conducting business in China outweigh the challenges as the country’s economy develops and becomes more open to global businesses.
China is a nation evolving quickly, and its marketplaces are developing quickly. No one strategy works for all international businesses entering China. Elements like the industrial sector, product type, company size, culture, long-term objectives, and global vision will determine each firm’s strategy.
The essential factors for businesses entering the Chinese market have been addressed in this white paper. Even though each company may have different specific plans, the paper offers suggestions to help businesses choose the right strategy for China. Companies may improve their chances of success in this dynamic and exciting market by recognizing the specific peculiarities of the Chinese market and developing tactics accordingly. Get in touch with Nakatomi so we can help you build your future.
Sources Links:
https://hbr.org/2019/05/what-western-marketers-can-learn-from-china
https://redferndigital.cn/landing/?gclid=EAIaIQobChMI9JHf6J_B_wIVJxEGAB1t7gpHEAMYASAAEgJv9PD_BwE
https://images.forbes.com/forbesinsights/StudyPDFs/Marketing_to_the_Chinese_Consumer.pdf
https://hbr.org/2021/09/should-you-localize-your-product-for-the-chinese-market